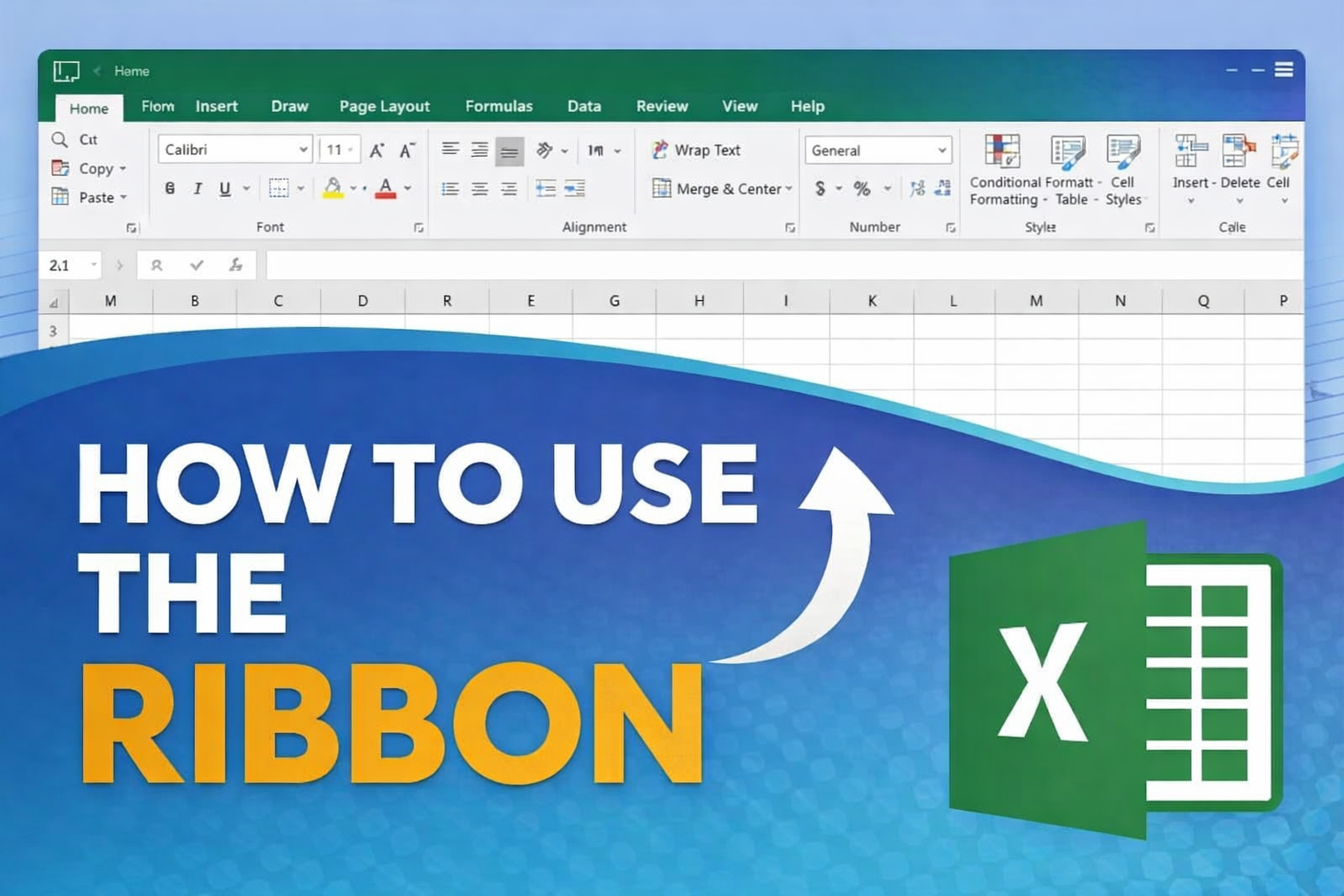
If you are new to Excel, the Ribbon may feel confusing at first. Once you understand how it is organized, however, you will find that almost every Excel task becomes easier and faster.
The Ribbon is the main place where Excel keeps its tools. Learning how to use it properly is one of the most important skills for anyone working with spreadsheets.
Table of Contents
What the Ribbon Is and Why It Matters
The Ribbon is the horizontal bar at the top of the Excel window. It contains all the commands you need to format data, build formulas, analyze information, and manage your workbook.
Excel opens with the Home tab selected by default because it includes the tools people use most often, such as copy, paste, formatting, and alignment.
Once you know where things are on the Ribbon, you stop wasting time searching for commands.
Understanding Ribbon Tabs
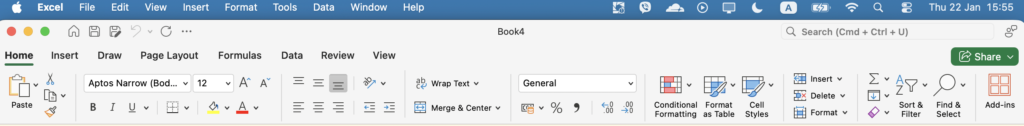
The Ribbon is divided into tabs, and each tab groups tools by task.
The most common tabs you will use are:
- File – For opening, saving, printing, and sharing files
- Home – For editing, formatting, and basic data work
- Insert – For tables, charts, images, and other objects
- Page Layout – For page setup and printing options
- Formulas – For functions and formula tools
- Data – For sorting, filtering, and data validation
- Review – For comments, spelling, and protection
- View – For worksheet views and window settings
You do not need to memorize everything. Over time, you naturally learn which tab to use based on what you want to do.
How Ribbon Groups Work
Inside each tab, commands are organized into groups.
Each group contains related tools.
For example:
- On the Home tab, formatting tools are grouped together
- On the Insert tab, charts and tables are in separate groups
- On the Data tab, sorting and filtering tools appear side by side
Group labels help you quickly scan and locate the right command.
Using the Ribbon: A Practical Example
Let’s walk through a simple task using the Ribbon: creating a table.
Steps
- Open an Excel file that contains data
- Click any cell inside the data range
- Select the Insert tab
- In the Tables group, click Table
Excel will automatically select the data for you.
- Confirm that My table has headers is checked
- Click OK
Your data is now converted into a table.
Why Tables Are Useful
When data is in a table:
- Sorting and filtering become much easier
- Formatting stays consistent
- Formulas adjust automatically as data grows
This is one of the reasons the Ribbon is so powerful: common tools are always within reach.
Switching Tabs and Working Faster
You can move between Ribbon tabs using:
- Your mouse
- Keyboard shortcuts such as Alt + H (Home) or Alt + N (Insert)
Learning a few shortcuts can save a surprising amount of time.
How to Hide or Show the Ribbon
If you want more space on your screen, you can collapse the Ribbon.
To collapse the Ribbon
- Right-click anywhere on the Ribbon
- Select Collapse the Ribbon
or - Press Ctrl + F1
When collapsed, the tabs remain visible. Clicking a tab temporarily shows the commands.
Tips from Everyday Excel Work
- Spend time exploring the Home, Insert, and Data tabs first
- Use group labels as visual guides
- Collapse the Ribbon when working on small screens
- Practice common tasks until Ribbon navigation feels natural
Conclusion
Knowing how to use the Ribbon in Excel is not about memorizing every button. It is about understanding how Excel organizes its tools. Once that structure makes sense, everything else becomes easier.
If you are serious about learning Excel, mastering the Ribbon is the best place to start.