In Excel, a workbook is a collection of worksheets stored in a single file. Every Excel file you create or open is a workbook. Whenever you start a new project in Excel—whether it’s tracking data, creating reports, or managing records—you work inside a workbook.
You can begin working with a workbook in different ways: by creating a blank file, using a ready-made template, or opening an existing workbook.
Table of Contents
What Is a Workbook in Excel?
A workbook is the main Excel file that contains:
- One or more worksheets
- Data, formulas, and formatting
- Charts, tables, and settings
In simple terms:
A workbook is the file, and worksheets are the sheets inside that file.
Creating a New Workbook
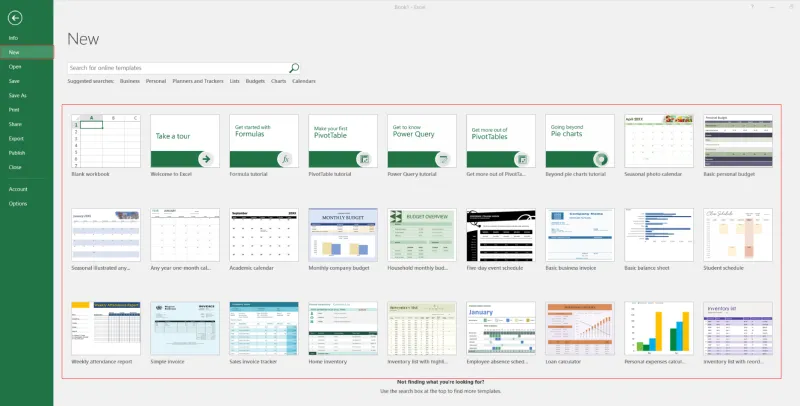
Excel gives you more than one way to start a new workbook.
Steps to Create a Blank Workbook
- Open Microsoft Excel
- Click File in the top-left corner
- Select New
- Choose Blank Workbook
- Or select a pre-designed template if needed
A new blank workbook opens on your screen, ready for use.
📌 Note: Excel automatically opens a new blank workbook when you launch the program.
Entering Text in Excel Cells
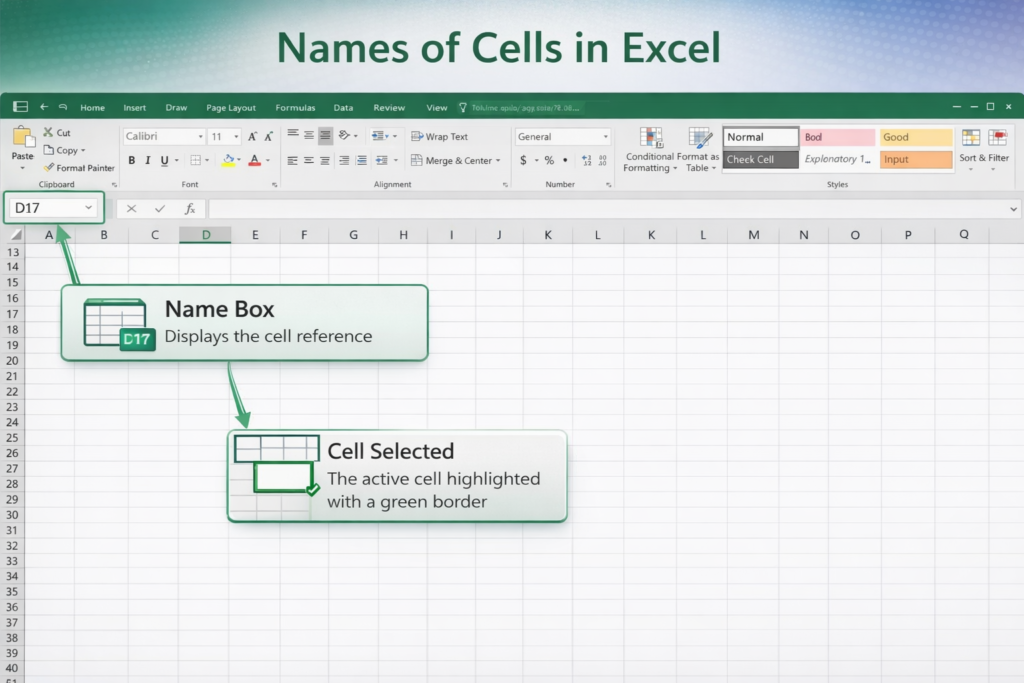
Excel worksheets are made up of rows and columns. Each intersection of a row and a column is called a cell.
Understanding Cell Addresses
- Columns are labeled with letters (A, B, C, …)
- Rows are labeled with numbers (1, 2, 3, …)
- A cell address combines both (for example: A1, C5)
When you click a cell, its address appears in the Name Box, located to the left of the formula bar.
Steps to Enter Text
- Click the cell where you want to enter data
- Type using your keyboard
- Press Enter
Whatever you type in the cell also appears in the Formula Bar for that cell.
Navigating Around a Worksheet
Excel provides several keyboard options to move around quickly.
- Tab → Move one cell to the right
- Shift + Tab → Move one cell to the left
- Arrow keys → Move up, down, left, or right
- Page Up / Page Down → Move vertically through the worksheet
(On laptops, you may need to hold Shift with these keys)
Learning basic navigation saves time when working with large datasets.
Saving the Workbook
Saving your workbook ensures your work is not lost.
Save for the First Time
- Click File
- Choose Save As
- Select a location
- Enter a file name
- Click Save
Save an Existing Workbook
- Click Save
- Or press Ctrl + S
Use Save As if you want to rename the file or save a copy in a different location.
Renaming a Worksheet in a Workbook
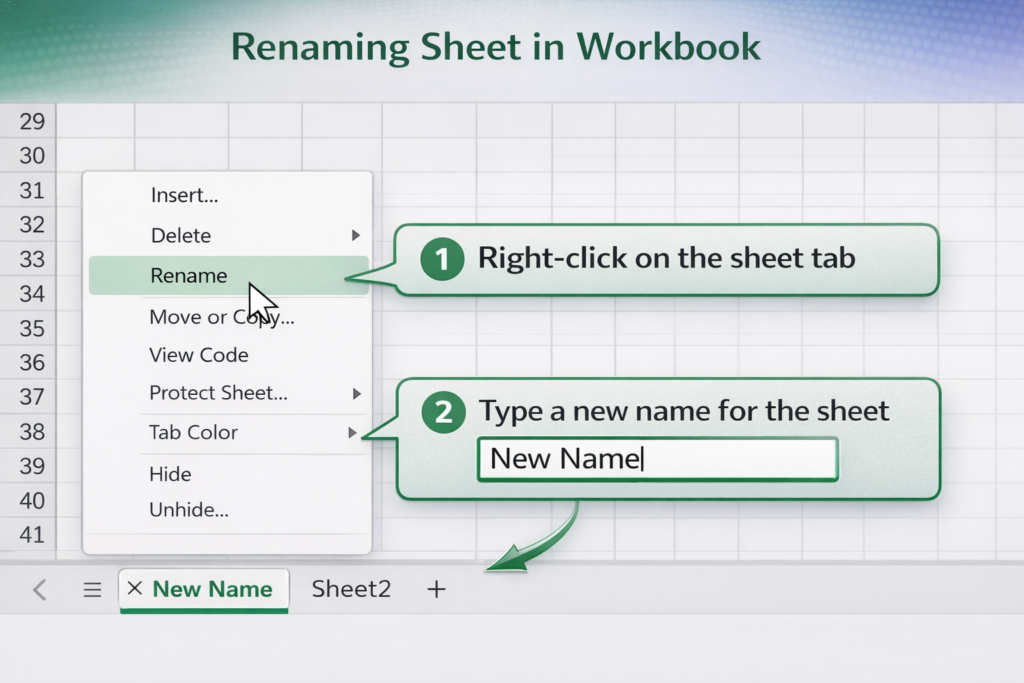
When a new workbook is created, Excel assigns default names like Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3. You can rename them to make your workbook easier to understand.
Steps to Rename a Worksheet
- Open the workbook
- Locate the sheet tabs at the bottom of the Excel window
- Double-click the sheet tab you want to rename
- Type the new name
- Press Enter
📌 Important notes:
- Sheet names can be up to 31 characters
- You cannot use special characters such as
/ \ ? * [ ]
Deleting a Workbook
If a workbook is no longer needed, you can delete it from your computer.
Steps to Delete an Excel Workbook
- Make sure the workbook is closed
- Open File Explorer (Windows key + E)
- Navigate to the folder where the file is saved
- Right-click the Excel file (
.xlsxor.xls) - Select Delete
⚠️ Deleted files go to the Recycle Bin unless permanently removed.
Why Understanding Workbooks Matters
Knowing how workbooks work helps you:
- Organize projects properly
- Manage multiple worksheets efficiently
- Save, rename, and delete files safely
- Avoid confusion between files and sheets
Conclusion
A workbook is the foundation of everything you do in Excel. Once you understand how to create, save, navigate, and manage workbooks, working with Excel becomes much easier and more organized.
Mastering this basic concept is an essential step for anyone learning Excel seriously.